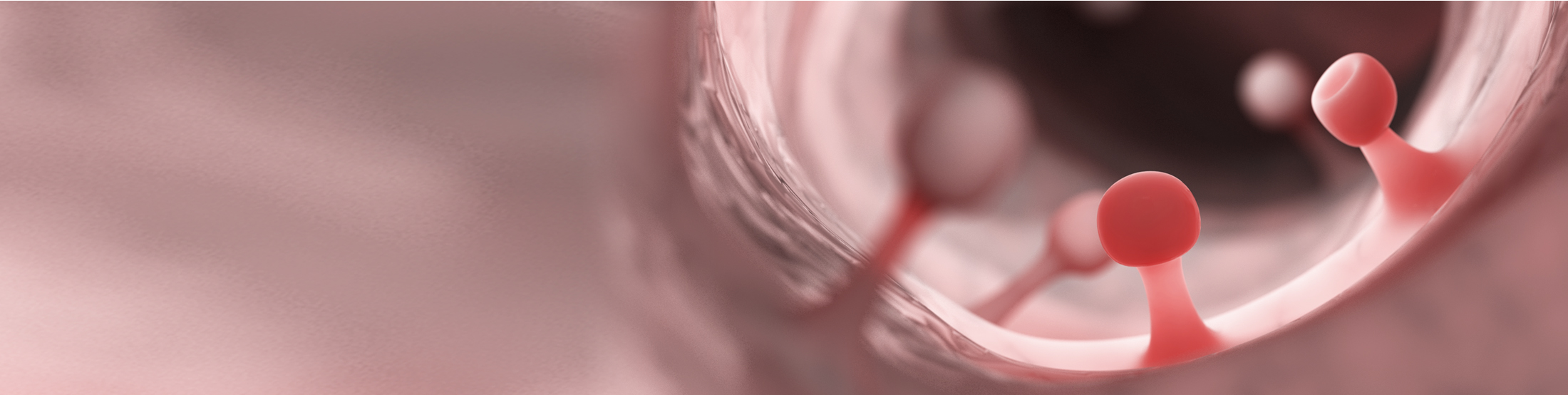
Colonic Polypectomy
- Most colorectal cancers develop through a gradual sequence of polyp growth
- Colorectal cancer mortality can be significantly reduced by colonoscopy and colonic polypectomy
- 19 million colonoscopies are performed in the US each year
- Expected incidence of pre-malignant polypoid lesions is around 30%
- 5 % of colonic polyps are laterally spreading lesions (LSLs)
- LSLs larger then 20mm are considered high risk precursors of CRC
- 5 million polyps are discovered each year, in the US, of which around 300,000 are LSLs
Current Practice
- LSLs are diagnosed during routine screening or surveillance colonoscopies
- In most cases patient is referred to an expert endoscopists for removal of LSLs
- Selection of removal technique requires lesions to be categorized based on location, size, morphology, pit pattern and vascular pattern
- Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR), Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD) and Surgical Therapy are some of the available treatment options for polypectomy
- LSL removal is technically demanding, requires highly trained personal and specialized equipment
- Operating time can range from 2-5 hours for removal of a single LSL
PLP-33 Formulation
- A Novel formula for treatment of LSL Polyps: 'pre' and 'post' polypectomy
- Formula demonstrated significant synergistic antitumor effect in pre clinical studies
- Preclinical POC validation
- Upcoming in-vivo studies
- Dossier preparation for submission of Pre-IND meeting request with FDA